Description
Planning to start an e-waste recycling business? You’ll need a thorough e waste recycling plant project report. This article covers market analysis, financial planning, and legal compliance. Learn the best practices for creating a successful project report.
Key Takeaways
Table of Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Understanding E-Waste Recycling
- 3 Market Analysis for E-Waste Recycling Plant
- 4 Legal Framework and Compliance
- 5 Key Components of a Project Report
- 6 Financial Planning and Investment
- 7 Process Flow and Technology
- 8 Environmental and Health Considerations
- 9 Profitability and Revenue Streams
- 10 Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- 11 Case Studies and Success Stories
- 12 Challenges and Risks
- 13 Future Trends and Innovations
- 14 Creating a Sustainable Business Model
- 15 Summary
- 16 Frequently Asked Questions
- 17 Why Buy Our E-Waste Recycling Plant Project Report?
- E-waste recycling is essential to mitigate environmental and health hazards posed by discarded electronic devices, recovering valuable materials and promoting a circular economy.
- The e-waste recycling market shows significant growth potential, with a projected CAGR of 13.1%, driven by increasing electronic device sales and consumer awareness.
- Compliance with regulations like the E-Waste Management Rules and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is vital for legal operation and effective management of e-waste recycling facilities.
Understanding E-Waste Recycling
E-waste refers to discarded waste electrical or electronic devices, encompassing everything from:
- old smartphones
- laptops
- defunct refrigerators
- televisions
The sheer volume of e-waste generated annually is staggering, with millions of tons of such waste produced globally. This not only poses a significant environmental challenge but also a health hazard due to the toxic substances these devices contain.
The importance of e-waste recycling cannot be overstated. Recycling e-waste is vital to prevent harmful materials, such as lead and cadmium, from contaminating the environment and affecting public health. The process of recycling e-waste recovers valuable materials, reducing the reliance on non-renewable resources and supporting a circular economy. However, the presence of toxic components in e-waste, if improperly managed, poses serious health risks.
The recycling process begins with the collection of old electronics through various methods like designated bins or community events. Once collected, e-waste is sorted manually to remove items needing special handling before being shredded into smaller pieces. Advanced separation techniques then recover valuable materials like metals and plastics. Utilizing certified e-waste recyclers ensures responsible disposal and recovery of these materials. The entire e waste recycling process not only helps in material recovery but also reduces the environmental footprint of electronic waste.
Consumer education and awareness about sustainable disposal options are expected to increase, influencing purchasing and recycling behaviors. Advocating for products designed for recyclability can enhance the efficiency of e-waste recycling processes. Understanding the significance of responsible e-waste disposal allows everyone to contribute to a more sustainable future.
Market Analysis for E-Waste Recycling Plant

The economic potential of the e-waste recycling market is immense. In 2019, the global value of discarded e-waste was estimated at over $57 billion, underscoring the financial opportunities in this sector. The market for electronics recycling is poised for significant growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.1%, expanding from $35 billion in 2023 to $120 billion by 2033.
The rising sales of electronic devices, driven by technological advancements and increasing disposable income, are contributing to the rapid growth of e-waste. Consumer electronics accounted for 40% of the global e-waste recycling market share in 2022, highlighting their significant contribution to recycling initiatives. However, only a small fraction of e-waste is currently recycled, with about 17.4% processed in 2019, indicating significant room for improvement.
Regionally, the Asia Pacific is expected to witness a growth rate of 8.5% in the e-waste recycling market over the next decade. As e-waste volumes increase, material recovery facilities (MRFs) must improve their processing efficiency to meet the rising demand. Effective market analysis, including current trends, demand, and potential future growth, is essential for any e-waste recycling business to thrive.
Legal Framework and Compliance
Compliance with local and international regulations is crucial for the operation of an e-waste recycling plant. The E-Waste Management Rules, 2022, mandate proper handling and disposal of electronic waste, outlining the responsibilities of producers, recyclers, and consumers. Compliance involves acquiring necessary permits from environmental authorities and adhering to strict handling protocols.
The Basel Convention aims to control hazardous waste movements, including e-waste, to protect human health and the environment. Organizations must obtain Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) authorization to operate legally in e-waste management, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This includes reporting their e-waste management practices to regulatory bodies like the Central Pollution Control Board in India.
Internationally, countries like Taiwan mandate that manufacturers design products with recycling in mind, ensuring responsibility for e-waste disposal and collection systems. However, the lack of consistent international regulations poses a significant obstacle to establishing standardized e-waste recycling practices. Understanding and navigating these legal frameworks is essential for any e-waste recycling venture.
Key Components of a Project Report
A well-crafted project report is essential for the success of an e-waste recycling plant. The executive summary is crucial as it encapsulates the main objectives and findings, providing a snapshot of the entire document. It should succinctly present the project’s purpose, scope, and key outcomes for quick comprehension.
In addition to the executive summary, the project report should detail personnel requirements, outlining the necessary skills and roles for efficient operations, including technical and managerial staff. A comprehensive description of the manufacturing process, including equipment and techniques, is also essential for operational clarity. These components ensure that the project report is thorough and provides a clear roadmap for the project’s implementation.
Financial Planning and Investment
Financial planning is a cornerstone of any successful e-waste recycling business. The initial financial requirement to establish an e-waste recycling plant is estimated to be between ₹45 to 50 lakhs, covering machinery and setup costs. For larger operations, the total capital investment can range from $1 million to $5 million, influenced by location and scale.
Operational costs, including utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses, typically range from $100,000 to $300,000 annually. Working capital needed to sustain operations before achieving profitability is estimated at around $100,000 to $300,000. A detailed financial plan should project costs, revenues, and profitability metrics over the business’s initial years, guiding investment decisions.
Effective financial planning can yield profitability margins of up to 20% in the e-waste recycling sector. Return on investment (ROI) can often be realized within three to five years, depending on market conditions and operational efficiency. Understanding these financial dynamics is crucial for the long-term success of the recycling business profitable.
Process Flow and Technology
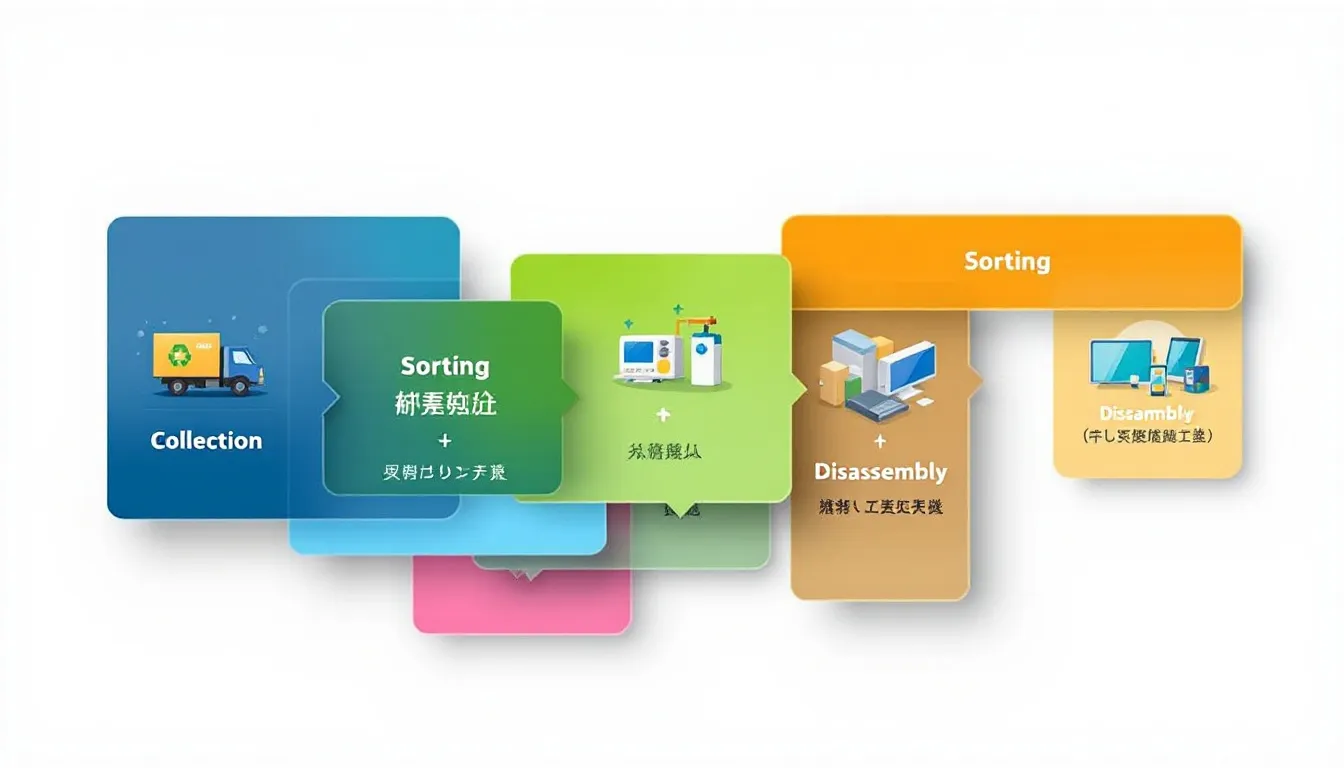
The treatment process of e-waste adheres to national guidelines. It also aligns with the best international practices. It begins with manual sorting, where workers remove items needing special handling, such as batteries, before the e-waste is shredded into smaller pieces. Advanced mechanical separation techniques, using magnets and eddy currents, segregate metals from plastics and glass during recycling.
Utilizing advanced recycling technologies can improve recovery rates and reduce waste, significantly impacting profitability. A detailed manufacturing process description, including equipment and techniques, is essential for operational clarity. These technological advancements ensure that the recycling process is both efficient and environmentally friendly.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Improper e-waste recycling can release numerous toxic substances, including neurotoxicants such as lead and mercury, into the environment. Informal recycling practices pose significant health risks, particularly to vulnerable populations like children and pregnant women. Health issues linked to improper e-waste recycling include adverse neonatal outcomes, neurodevelopmental delays, and respiratory problems in children.
Low- and middle-income countries often face heightened risks from e-waste due to insufficient regulations, infrastructure, and training for safe recycling. Toxic pollutants released during unsafe e-waste management can travel long distances, exposing distant communities to harmful substances.
Establishing safety protocols in e-waste recycling plants is essential to protect workers and the environment from hazardous materials found in electronic waste. There is a growing emphasis on ethical e-waste recycling, focusing on worker safety and environmentally responsible practices. Ensuring these considerations are met is crucial for the sustainable management of e-waste.
Profitability and Revenue Streams
E-waste recycling businesses can generate revenue not only from recycling but also from services like data destruction and refurbishing electronics. Devices that contain high-value materials, like smartphones and laptops, can lead to greater profitability due to the recovery of precious metals. To maximize benefits, it is essential to recycle e waste effectively.
Market prices for recovered metals such as gold and copper fluctuate, affecting the overall profitability of e-waste recycling businesses. Additionally, recycling can ease the pressure on the supply chain for materials like lithium, crucial for rechargeable batteries and electric vehicles. Understanding these revenue streams is essential for ensuring that the e-waste recycling business remains profitable.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a strategy aimed at minimizing the environmental effects of product waste, particularly electronics, by making manufacturers accountable for their products’ end-of-life disposal. The EPR system promotes a cradle-to-cradle approach, encouraging proper collection and recycling of electronic products instead of allowing them to end up in landfills.
Under EPR regulations, producers of electronic goods must collect and recycle a specified percentage of their products in an eco-friendly manner. Singapore’s legislation, for example, makes producers responsible for managing the lifecycle of electronic products, encouraging recycling and reuse.
Participating in manufacturer take-back programs aids in recycling initiatives and promotes ecological responsibility. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for the success of an e-waste recycling business.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Successful e-waste recycling initiatives provide valuable lessons and showcase best practices for effective waste management. For instance, Cambridge City Council introduced distinctive pink bins for collecting small electrical items, leading to the collection of 49 tonnes of e-waste since their deployment in 2022. This innovative approach has significantly improved the community’s e-waste recycling efforts.
In Egypt, the E-Tadweer app incentivizes e-waste disposal by allowing users to exchange unwanted electronics for vouchers to purchase new items. Similarly, the Royal Mint in the UK is developing a method to recover 99% of gold from discarded electronics through a sustainable chemical process. These success stories highlight the potential for innovative solutions to drive effective electronic waste recycling and e-waste management.
Challenges and Risks
Despite the potential benefits, the e-waste recycling market faces significant challenges. Insufficient collection facilities and high processing costs hinder effective recycling efforts. These challenges make it difficult to establish a comprehensive e-waste management system.
The complexity of electronic products adds another layer of difficulty, making the separation and sorting of materials during recycling a significant challenge. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions and substantial investment in infrastructure and technology.
Future Trends and Innovations

The future of e-waste recycling is bright, with several trends and innovations poised to transform the industry. The integration of advanced technologies, such as AI and robotics, in e-waste recycling can significantly enhance sorting efficiency and worker safety. Smart recycling solutions, like IoT-enabled bins, can optimize e-waste management by automating sorting and guiding proper disposal methods.
Material recovery techniques are evolving to reclaim valuable materials from e-waste using eco-friendly processes like bioleaching. Urban mining is expanding the concept of recovering valuable materials from a wider range of waste streams, beyond just e-waste.
The circular economy model is projected to see revenue growth from $339 billion in 2022 to $713 billion by 2026, reflecting increased investment in sustainable practices. Major tech companies are focusing on creating modular products to simplify repair processes and extend product lifecycles. Localizing e-waste recycling services is becoming more common, reducing transportation costs and promoting community engagement.
These trends indicate a greener future for e-waste recycling.
Creating a Sustainable Business Model
Creating a sustainable business model for e-waste recycling involves promoting consumer awareness regarding the impact of electronic purchases. Opting for minimal electronic purchases can significantly decrease e-waste, encouraging consumers to buy only necessary devices. Choosing durable and repairable electronics supports sustainability by reducing the frequency of replacements.
The final stage of e-waste processing involves recovering and preparing separated materials for reuse, contributing to a circular economy. By focusing on these aspects, businesses can develop a responsible and profitable e-waste recycling model.
Summary
In conclusion, crafting a comprehensive project report for an e-waste recycling plant involves understanding the market, adhering to legal frameworks, planning financials, and incorporating advanced technologies. Addressing environmental and health considerations, exploring profitability and revenue streams, and focusing on sustainable practices are key to success. By following these best practices, we can create a greener future and ensure responsible e-waste management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is e-waste?
E-waste is defined as discarded electrical or electronic devices, including items like old smartphones, laptops, televisions, and refrigerators. Proper disposal and recycling are essential to mitigate its environmental impact.
Why is e-waste recycling important?
E-waste recycling is essential to safeguard the environment and public health by preventing the release of toxic substances. Moreover, it recovers valuable materials, contributing to a sustainable circular economy.
What are the financial requirements for starting an e-waste recycling plant?
To start an e-waste recycling plant, expect initial financial requirements of approximately ₹45 to 50 lakhs for smaller operations, or between $1 million to $5 million for larger setups, depending on the location and scale of your business. It is vital to assess your business model carefully to ensure adequate funding.
What are some challenges faced by the e-waste recycling industry?
The e-waste recycling industry faces significant challenges such as inadequate collection facilities, high processing costs, and the complex task of separating and sorting materials. Addressing these issues is crucial for enhancing recycling effectiveness.
What is Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)?
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) mandates that manufacturers take responsibility for the disposal of their products at the end of their life cycle, promoting proper collection and recycling to reduce environmental harm. This approach fosters accountability and encourages sustainable practices within the industry.
Why Buy Our E-Waste Recycling Plant Project Report?
Comprehensive Analysis: Our project report provides a detailed analysis of the e waste recycling market, including current trends, demand forecasts, and growth opportunities. This comprehensive insight helps you make informed decisions about entering the e waste business.
Expert Guidance: Compiled by industry experts, the report offers guidance on setting up an e waste recycling plant, including legal compliance, financial planning, and operational strategies. It ensures you have the necessary knowledge to start an e waste recycling business effectively.
Financial Planning Tools: With detailed financial projections and investment requirements, our report equips you with the tools needed to plan your budget and assess the profitability of your e waste recycling venture. This includes insights into initial capital investment and operational costs.
Regulatory Compliance: Understanding and adhering to local and international regulations is crucial. Our report outlines the necessary legal frameworks, such as the E-Waste Management Rules and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), ensuring your business operates within legal boundaries.
Technological Insights: Stay ahead of the curve with information on the latest recycling technologies and processes. Our report covers advanced methods for efficient e waste recycling, helping you implement cutting-edge solutions in your plant.
Environmental and Health Considerations: The report emphasizes the importance of environmentally responsible practices and health safety measures, ensuring your recycling operations do not pose risks to human health or the environment.
Profitability and Revenue Streams: Discover potential revenue streams beyond recycling, such as data destruction and refurbishing electronics. Our report helps you identify opportunities to maximize profitability in the e waste recycling sector.
Success Stories and Case Studies: Learn from successful e waste recycling initiatives worldwide. Our report includes case studies that provide valuable insights and best practices to inspire and guide your business journey.
Sustainable Business Model: Our project report promotes a sustainable approach to e waste recycling, encouraging practices that support a circular economy and reduce environmental impact. This ensures your business contributes positively to the planet.








