Why and how to set up a lithium-ion battery recycling business in India? With the rise in electric vehicles and sustainability efforts, this business is vital. This article explains the importance, market potential, and step-by-step processes to start your own recycling plant in India.
Key Takeaways
- Lithium-ion battery recycling is essential for environmental sustainability, resource conservation, and economic growth through job creation in India.
- The market for lithium-ion battery recycling in India is projected to grow significantly due to increasing electric vehicle adoption and government initiatives.
- Setting up a recycling business involves careful planning, including legal compliance, machinery investment, and establishing a reliable supply chain for raw materials.
Importance of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling
Recycling lithium-ion batteries is vital for maintaining environmental sustainability. This practice significantly reduces landfill waste, promoting efficient resource management. This not only conserves natural resources but also minimizes environmental degradation by cutting down on the need for mining raw materials. Moreover, recycling helps prevent the release of toxic materials into the environment, thereby protecting ecosystems and human health.
Decreasing landfill waste diminishes environmental pollution and conserves natural resources. Recycling lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to producing new batteries from raw materials.
The battery recycling sector can drive economic growth by creating diverse job opportunities. This can significantly lessen financial burdens associated with waste management by diverting toxic batteries from landfills, minimizing potential environmental damage and cleanup costs. Additionally, battery recycling companies play a crucial role in this process.
Lithium-ion battery recycling is key to protecting the environment while fostering economic growth through job creation and cost savings. The business potential and opportunities for entrepreneurs in this sector are immense, making it a worthwhile venture.
Market Potential in India
In 2023, India’s lithium-ion battery recycling market was valued at approximately USD 1.97 billion. The market is expected to grow annually by around 9.8% from 2024 to 2030, indicating significant expansion. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles is driving this growth, amplifying the demand for efficient battery recycling solutions. As the Asia Pacific region is anticipated to hold the largest market share for battery recycling, India stands to benefit hugely from this trend.
The automotive segment, particularly related to electric vehicles, is a major source for battery recycling. Government initiatives pushing for a 30% electric vehicle fleet by 2030 further enhance the demand for ev batteries recycling. Rising investments in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems are creating opportunities for importing used batteries for recycling, stabilizing raw material prices, and reducing supply shortages.
Operating battery recycling facilities requires a skilled workforce, contributing to local job creation and economic stability. A recycling facility can create direct jobs in operations and indirect jobs in transportation and logistics. This makes lithium-ion battery recycling a promising sector for employment generation and economic growth in India.
Why Set Up a Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Business in India?

Rapid industrialization and the adoption of electric vehicles are driving the growing demand for effective battery recycling solutions. Setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling business in India is a strategic move, supported by various government incentives and policies aimed at promoting the recycling industry. This not only helps in managing battery waste but also mitigates the high dependency on imports for raw materials.
In India, recycling lithium-ion batteries presents significant environmental and economic benefits. It helps conserve natural resources, reduces environmental degradation, and promotes sustainable practices. The recycling process aids in recovering valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite, which are essential for producing new batteries. This closed-loop system not only supports sustainability but also ensures a steady supply of raw materials for battery production.
Entrepreneurs and businesses in the lithium-ion battery recycling sector can capitalize on growing market demand, government support, and contribute to environmental conservation. Economic viability combined with environmental responsibility makes this a compelling business opportunity.
Understanding Lithium-Ion Batteries

Lithium-ion batteries are a marvel of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles. They work by allowing lithium ions to move freely between electrodes, generating an electric current. One of the main advantages of lithium-ion batteries is their high energy density, which makes them suitable for various applications. As a type of rechargeable battery, they can be reused after charging, providing both convenience and efficiency.
The key components of lithium-ion batteries include lithium metal oxides for the cathode and carbon materials for the anode. Graphite is a common choice for anode materials. For cathodes, options may include lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate. Different types of lithium-ion batteries, such as Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), Lithium Titanate Oxide (LTO), and Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA), are used based on their specific properties and applications.
Understanding lithium-ion battery composition and functioning is crucial for efficient recycling. Each battery type has unique characteristics that influence the recycling process, requiring tailored methods for specific battery chemistries.
Understanding the Basics: Lithium-Ion Battery Composition
Lithium-ion batteries are composed of several key materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, and graphite. These materials are crucial for battery performance and are valuable resources recoverable through recycling. For instance, lithium is critical for the battery’s energy density and charge capacity, while cobalt is used in the cathodes to enhance stability and performance.
Recovering these metals through recycling conserves natural resources and reduces the environmental impact of mining. By understanding the chemical composition of lithium-ion batteries, recyclers can develop efficient processes to extract and reuse these materials, contributing to a more sustainable battery production cycle.
Steps to Set Up a Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Plant

Setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling plant involves critical steps like site selection and acquiring necessary machinery. Each step requires careful planning and execution to ensure efficient operation and legal compliance.
Site Selection and Land Finalization
Choosing the right location for the recycling plant is crucial. The site should be strategically located near sources of battery waste to minimize transportation costs and ensure a steady supply of raw materials. Additionally, the site must comply with zoning laws and environmental regulations to avoid legal complications. Battery recycling plants should also be considered in the planning process.
Proximity to key stakeholders, such as battery manufacturers and collection agencies, can streamline operations and enhance the efficiency of the supply chain. Ensuring community acceptance and adhering to local regulations are also vital considerations when finalizing the site for your recycling plant.
Required Machinery and Equipment
Setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling plant requires a range of machinery and equipment. Essential machinery includes shredders, separators, and smelting systems, which are used to break down and process the batteries. Additional equipment like granulators and air separators help in the efficient extraction of valuable materials from the battery components.
High-quality, reliable machinery is essential for smooth plant operation. Each equipment piece plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and safe recovery of valuable materials.
Raw Materials and Supply Chain
The key raw materials needed for lithium-ion battery recycling include:
- Lithium
- Cobalt
- Nickel
- Graphite
These materials are recovered from used batteries and are essential for producing new batteries, thus closing the loop in the battery manufacturing process. Lithium, in particular, is crucial for the battery’s performance, while cobalt is highly valued for its role in the cathodes.
A reliable supply chain is vital for the success of a recycling plant. This involves developing relationships with battery retailers, manufacturers, and collection agencies to ensure a consistent flow of used batteries. Effective logistics, partnerships with local recycling networks, and regulatory adherence contribute to an efficient supply chain.
A well-organized supply chain ensures that the plant operates smoothly and efficiently, minimizing disruptions and maximizing the recovery of valuable materials from waste batteries.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Legal compliance is critical for setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling plant. This involves obtaining the necessary registrations, authorizations, and consents from various regulatory bodies.
Following environmental regulations and safety standards ensures sustainable plant operation.
Battery Waste Management Rules
The new Battery Waste Management Rules replace the Batteries (Management and Handling) Rules, 2001, and cover all battery types, including those used in electric vehicles and automotive applications. The E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016 outline the duties of recyclers. This includes specific responsibilities related to lithium-ion batteries. These rules mandate recyclers to ensure the safe handling, storage, and disposal of waste batteries to prevent environmental contamination.
All lithium-ion batteries must be documented and marked for traceability before transportation. Recyclers must ensure that their processes do not adversely affect health or the environment, adhering to stringent safety and environmental standards. Proper classification and hazardous waste management are essential for regulatory compliance.
State Pollution Control Board Approvals
Obtaining the necessary approvals from the State Pollution Control Board is essential for compliance with environmental regulations. This includes both Consent to Establish and Consent to Operate, ensuring that the recycling plant meets all environmental and safety standards.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Under the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework, producers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of batteries, from collection to recycling. This framework prohibits landfill disposal and mandates the collection and recycling of waste batteries. Technical guidelines and standard operating procedures (SOPs) are being developed to ensure the effective implementation of EPR regulations.
By adhering to EPR regulations, producers and recyclers can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly battery recycling industry. This framework promotes responsible disposal and encourages the development of new recycling technologies.
Investment and Financial Feasibility
Assessing financial feasibility involves analyzing capital investments, operating costs, and revenue streams.
Accurate financial projections are essential to secure funding and ensure the sustainability of the business.
Initial Capital Investment
Setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling facility requires substantial initial capital for land acquisition, machinery, and documentation. The total capital cost is composed of direct costs, such as infrastructure and equipment, and indirect costs, including project management and insurance. Additionally, contingency funds must be allocated to cover unexpected expenses.
Initial approvals and licenses cost between Rs. 1,000 and Rs. 7,00,000, depending on business scale. Overall, setting up a recycling plant in India can cost between $90,000 and $370,000, influenced by factors such as machinery prices, plant size, and operational costs.
High-quality machinery investment, ranging from $70,000 to $350,000, ensures efficient processing and long-term profitability.
Operating Costs and Revenue Streams
Ongoing operating costs for a lithium-ion battery recycling plant include labor, utilities, maintenance, and material handling. Labor costs are approximately Rs. 500 per employee, contributing to the overall operational budget. Other significant expenditures include transportation, power consumption, and the cost of chemicals and consumables required for the recycling process.
Selling recovered materials like cobalt, nickel, and lithium generates revenue. These materials are in high demand for producing new batteries, making them valuable commodities. Profits from recycling operations can vary based on battery chemistry, with NMC and NCA batteries generally offering higher revenue due to their valuable metal content. Additionally, government incentives and subsidies are available for businesses engaging in battery recycling, enhancing financial viability.
Achieving economies of scale is crucial for the profitability of a battery recycling business. Specific annual capacities are needed for different recycling technologies to maximize efficiency and revenue generation. Accurate financial modeling and cash flow analysis are essential for assessing the sustainability and growth potential of the recycling business.
Manufacturing Process of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling
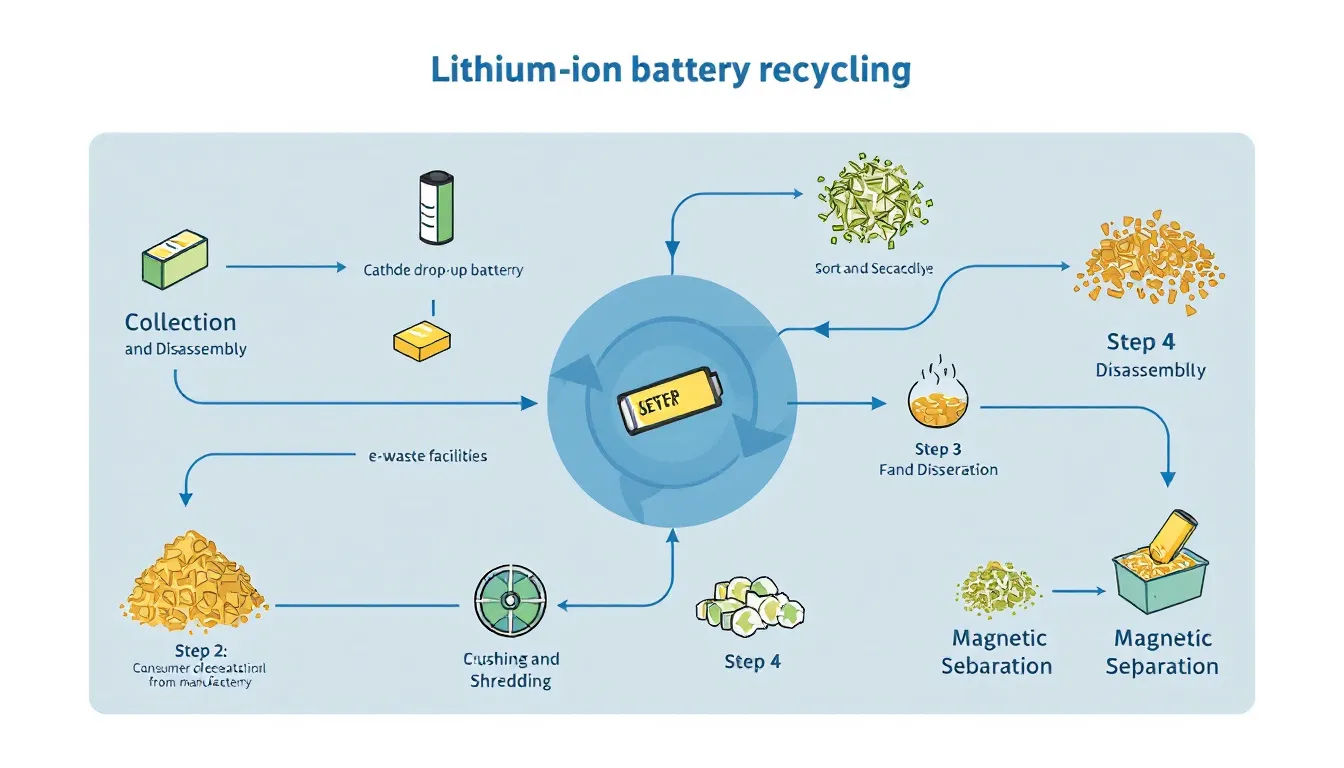
Lithium-ion battery recycling processes involve key steps: collection and transportation, mechanical processing, and chemical extraction. Each step is designed to efficiently recover valuable materials from waste batteries while ensuring compliance with environmental and safety standards. Additionally, li ion battery recycling plays a crucial role in this process.
Collection and Transportation
Effective collection methods include drop-off centers, collection drives, and partnerships with retailers and manufacturers. These methods ensure a steady supply of waste batteries for direct recycling.
Transporting used batteries requires planning for safety and legal compliance, minimizing leak or spill risks. Transportation of lithium-ion batteries must adhere to hazardous material regulations to prevent accidents and ensure safe handling.
Proper packaging, labeling, and documentation are essential to comply with regulatory requirements and ensure the safe and efficient transport of used batteries to the recycling facility.
Mechanical Processing
Mechanical processing is crucial in lithium-ion battery recycling. It involves dismantling batteries to extract valuable components like plastic and metals. The dismantling process is essential for obtaining key battery components like the anode, cathode, and electrolyte, which are necessary for recycling. Size reduction of batteries helps optimize the extraction process by breaking them into smaller pieces, facilitating the recovery of metals.
Techniques like air separation and eddy current recover materials like aluminum and copper. These methods effectively separate valuable materials based on their physical properties, ensuring efficient and cost-effective recycling.
Chemical Extraction
Chemical extraction primarily involves hydrometallurgy, using aqueous solutions to extract metals from battery waste. The ‘black mass’ produced during battery recycling contains critical resources like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Specific chemical techniques are used to extract lithium from the battery powder, ensuring the recovery of this valuable material.
Pyrometallurgy, a method utilizing heat, is another approach for extracting metals from battery components. Hydrometallurgical processes refine the black mass to extract valuable metals for reuse, contributing to the sustainability of the recycling process.
Environmental and Safety Standards
Adhering to environmental and safety standards is crucial for the sustainable operation of a lithium-ion battery recycling plant. Compliance with the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, ensures environmentally responsible management of waste batteries.
These regulations mandate producers to ensure the collection and recycling of waste batteries, promoting environmental sustainability and minimizing pollution.
Hazardous Waste Management
Proper management of hazardous waste is essential in lithium-ion battery recycling. Used batteries are collected from various consumer electronics such as smartphones and electric vehicles, ensuring careful transportation to prevent leakage. Once deemed safe for reuse, these batteries are prepared for safe transport.
Segregation and treatment of hazardous waste are critical to prevent environmental contamination during recycling. Best practices for hazardous waste management include proper storage, labeling, and transportation to reduce fire risks and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Safety Standards and Worker Training
Comprehensive safety training programs for workers handling lithium-ion batteries prevent accidents and ensure safe operations. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory to ensure worker safety in battery recycling operations. Regular emergency drills and clear response plans are necessary to prepare workers for potential incidents during battery recycling operations.
By adhering to stringent safety standards and providing thorough training, recycling facilities can minimize health risks associated with exposure to hazardous materials and ensure a safe working environment for their employees.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Lithium-ion battery recycling has significant economic and environmental impacts. Recycling can recover up to 95% of the valuable materials from batteries, reducing the reliance on mining and conserving natural resources.
The industry can contribute to economic growth by generating jobs and improving local economies, while also minimizing the environmental impact of battery waste.
Job Creation and Local Economy
The establishment of lithium-ion battery recycling businesses creates numerous job opportunities in various roles, from collection and processing to management. As the recycling industry grows in response to rising battery waste, it fosters the development of specialized skill sets among the workforce. Employment in battery recycling contributes to higher local incomes and job stability, enhancing overall community welfare.
The recycling sector stimulates local economies through job creation, leading to increased spending in local businesses and services. The cumulative effect of job creation and economic stimulation encourages social development and community resilience against economic downturns.
Environmental Benefits
Recycling batteries preserves natural resources by reusing valuable materials, reducing reliance on mining. Proper battery recycling prevents hazardous materials from entering landfills, avoiding soil and water contamination.
Lithium-ion battery recycling plays a crucial role in enhancing environmental sustainability by reducing the negative impacts associated with battery waste. Overall, lithium-ion battery recycling contributes to a significant reduction in landfill waste and minimizes the carbon footprint associated with both mining and disposal.
By promoting a more sustainable future, battery recycling ensures that we protect our environment for generations to come.
Project Report Essentials
A well-structured project report clarifies business objectives and plans. It provides potential investors with detailed insights into the market analysis, technology, and financial feasibility of the battery recycling business.
Preparing a Comprehensive Project Report
Preparing a comprehensive project report involves covering critical aspects such as site development, machinery needs, raw materials, and utility requirements for the battery recycling process. The report should also encompass industry insights, feasibility studies, and detailed financial projections to attract potential investors. Including an industry introduction helps contextualize the project within the battery recycling landscape.
Financial projections must include estimated revenues, costs, and funding strategies to attract investors. A well-prepared project report can serve as a valuable tool for securing loans and funding for the recycling business.
Key Metrics and Financial Projections
Understanding key financial metrics, such as the initial investment required, ongoing operating costs, and potential revenue streams, is crucial for attracting investors and securing loans. These metrics clarify the financial viability and growth potential of the battery recycling business.
Import and Export Opportunities
Increasing demand for raw materials and sustainable practices drive the global market for used batteries, promoting recycling initiatives. India offers significant opportunities for importing used batteries due to its growing electric vehicle market and the need for sustainable waste management. Recyclers can capitalize on the high demand for recycled materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, in global markets.
Exporting these valuable materials can open up lucrative opportunities for Indian recyclers, contributing to the country’s economic growth and promoting sustainable practices on a global scale. The rise in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems further enhances the demand for recycled battery materials, making it a promising sector for import and export activities.
Challenges and Considerations
Setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling business involves unique challenges and considerations. Regulatory hurdles and environmental concerns must be navigated to ensure compliance and sustainability.
Technological challenges in recycling efficiently and handling hazardous waste require significant investment and expertise.
How Project Report Bank Can Assist You
Project Report Bank offers services, including downloadable project reports, to assist businesses in setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling plant. Their reports provide detailed information on industry introduction, feasibility, manufacturing process, financial analysis, and other necessary components to attract investors.
Utilizing the services of Project Report Bank can streamline the process of setting up a recycling business by providing expert insights and comprehensive guides. Their knowledge and in-depth articles can help entrepreneurs navigate the complexities of the battery recycling industry, ensuring a successful and sustainable business venture.
Summary
In summary, the lithium-ion battery recycling industry in India offers significant opportunities for economic growth and environmental sustainability. By setting up a recycling business, entrepreneurs can contribute to the conservation of natural resources, reduce landfill waste, and promote sustainable practices. The comprehensive guide provided in this blog covers all aspects of starting a recycling business, from understanding the basics of lithium-ion batteries to navigating legal and regulatory requirements.
We encourage you to explore the potential of the lithium-ion battery recycling sector and take advantage of the growing market demand and government support. With careful planning, investment, and adherence to environmental and safety standards, you can build a successful and sustainable recycling business that benefits both the economy and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key components of a lithium-ion battery?
The key components of a lithium-ion battery are lithium metal oxides for the cathode and carbon materials, like graphite, for the anode, often supplemented with cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These elements work together to enable efficient energy storage and transfer.
What are the initial capital costs for setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling plant in India?
The initial capital costs for setting up a lithium-ion battery recycling plant in India typically range from ₹75 lakh to ₹3.7 crore, influenced by factors such as land acquisition and machinery requirements. Investing in this venture can be substantial, so careful financial planning is essential.
What are the environmental benefits of recycling lithium-ion batteries?
Recycling lithium-ion batteries significantly reduces landfill waste, conserves natural resources, and lowers the environmental impact associated with mining and raw material extraction. This practice is essential for a sustainable future.
What legal approvals are required to set up a battery recycling plant?
To set up a battery recycling plant, you need to obtain registration and authorization from regulatory bodies, such as the State Pollution Control Board, to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Meeting these legal approvals is crucial for a successful operation.
How does Project Report Bank assist in setting up a recycling business?
Project Report Bank effectively assists in establishing a recycling business by offering downloadable project reports and expert insights, making it easier to navigate the complexities of setting up a recycling plant. This resource is invaluable for ensuring a structured and informed approach to your business launch.
